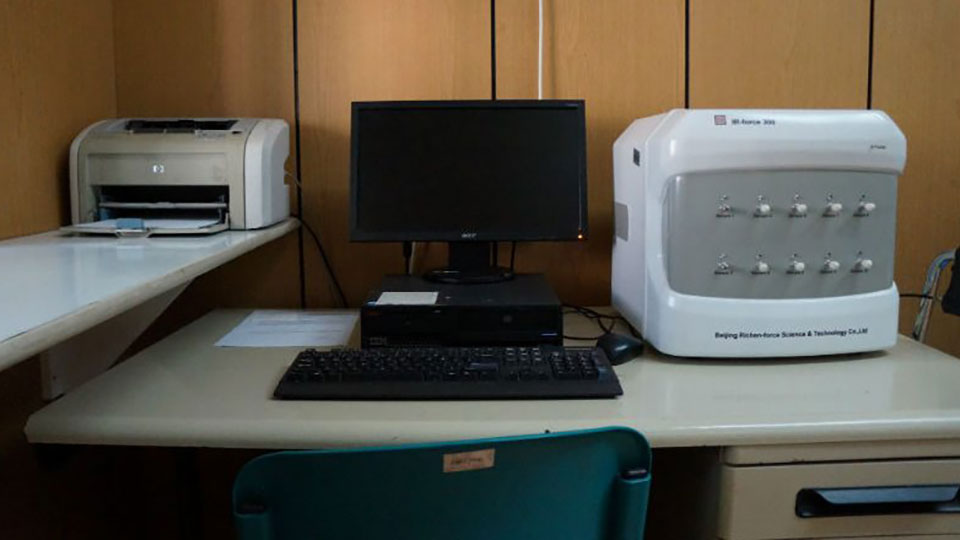
Urea breath test (UBT) belongs to the group of noninvasive tests for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection. It is based on the ability of Helicobacter pylori to hydrolyze urea to CO2 and ammonia. For this test, an isotope of carbon is administered orally, after which the release in the form of CO2 that can be registered in the exhaled air samples.
The University Clinic for Gastroenterology has 13C (carbon 13) non-radioactive tests. The sensitivity and specificity of this UBT is approximately 95-100%, respectively. From there false positives are very rare, and falsely negative results can be registered with inadequate application of the test.
In order to reduce false positive results, the following should be done:
Do not take antibiotics by any indication for a period of at least 4 weeks before taking the test.
Do not treat patients with proton pump inhibitors (PPI) and bismuth preparations at least two weeks prior making the test. H2 receptor antagonists are not contraindicated for the test.
In hospitalized patients with GIT bleeding (mainly ulcer bleeding), the test can be performed after the bleeding is stopped, that is, when the patient returns to oral food intake, and was not be treated with PPI.
Indications for UBT:
- Peptic ulcer disease, i.e. patients with stomach ulcer and duodenum
- Patients with proven MALT lymphoma
- Patients with a past history of ulcer disease confirmed with endoscopy
- Patients with long-term PPI therapy, such as those with severe forms of gastro esophageal reflux disease
- GERD) or patients on long-term therapy with antirheumatics
- Patients with functional dyspepsia
- Patients operatively treated of gastric cancer
- Asymptomatic patients with high positive (many family members) family history of gastric carcinoma
- Patients with immunologically mediated thrombocytopenia
- Patients with iron deficiency anemia that cannot be explained in any other way
- Patients with megaloblastic anemia that cannot be explained in any other way
Priority in testing have patients in whom control should be made to prove the effectiveness of the eradication therapy, where the presence of infection is based on a positive serum test or positive antigen test from feces for Helicobacter pylori.
There is no contraindication of the use of this test in pregnant women, nursing mothers, children and elderly patients. It is important to advise the patient not to eat on the day of testing and not to drink at least 2 hours before taking the test.


